Working with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition. We can't emphasize this enough.
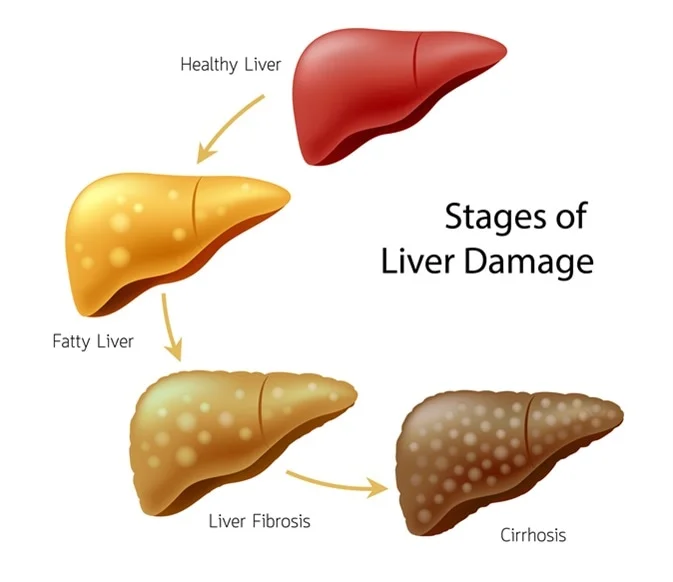
The treatment of the liver disease depends on the underlying cause of the disease. Overall, taking steps to improve liver health, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding toxins, can help prevent liver disease and improve liver function.
Working with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition. We can’t emphasize this enough.
General lifestyle changes and home remedies
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is also a risk factor for liver disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a healthy diet can improve liver health.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet that is high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources can help improve liver function. Avoiding processed and fatty foods can also help.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve liver health and reduce the risk of liver disease.
- Twenty-one minutes of daily walking can help. Emphasise on developing this habit
- Manage underlying health conditions: If you have underlying health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, it’s essential to manage them properly to prevent further damage to the liver.
- Get vaccinated: Certain viral infections, such as hepatitis A and B, can cause liver disease. Getting vaccinated against these viruses can help prevent liver damage.
- Reduce stress: Chronic stress can contribute to liver disease. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help improve liver health.
- Avoid
- Avoid alcohol: Alcohol is a significant cause of liver damage. If you have liver disease, it’s essential to avoid alcohol altogether.
- Avoid exposure to toxins: Avoid exposure to toxins that can damage the liver, such as cleaning products, chemicals, and insecticides. Use protective tools while handling dangerous chemicals
Types of liver disease:
There are many types of liver disease, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and cirrhosis. The underlying cause of the liver disease will determine the treatment plan.
Dietary recommendations:

A healthy diet for the liver includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. It’s important to limit or avoid processed foods, fried foods, sugary drinks, and alcohol. Drinking plenty of water can also help flush toxins out of the liver. A recent study called out the benefit of cloves.
Exercise recommendations:
Regular exercise can improve liver health by reducing inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Establishing a habit is the most important aspect.
Herbal supplements:
Some herbal supplements, such as milk thistle and turmeric, are believed to improve liver function. However, it’s essential to talk to a healthcare provider before taking any herbal supplements, as they can interact with other medications and may not be safe for everyone.
It’s essential to note that while these lifestyle changes can improve liver health, they may not be sufficient to treat advanced liver disease. If you have liver disease, it’s crucial to work with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Medical Interventions
- Medical treatments: In some cases, medication or other medical treatments may be necessary to manage the liver disease. For example, antiviral medications can be used to treat viral hepatitis, while immunosuppressant drugs can be used to treat autoimmune hepatitis.
- Liver transplant: A liver transplant may be necessary in severe cases of liver disease. This involves removing the diseased liver and replacing it with a healthy liver from a donor.
References & Similar Articles
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8744418/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-50352-4
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332221003735
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003986122001539
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30425782/